The liver is a critical organ that is essential for nourishment. It aids in digestion, eliminating toxins, metabolizing medications and alcohol, and creating proteins necessary for blood coagulation. Liver disease, often known as hepatic disease, refers to disorders that can affect your liver and impair its capacity to operate correctly.
Damage to your liver can build up over time as you progress through the phases of liver disease. Each stage has an impact on your liver’s capacity to operate normally. There are four stages of liver disease: inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis (Chronic Liver Disease or CLD), and end-stage liver disease (ELSD).
Liver disease, whether acute or chronic, can be dangerous to your health. Many factors can increase the chance of developing chronic liver and acute liver failure, including lifestyle, genetics, and drugs.
What is CLD?
Cirrhosis or CLD is a long-term condition in which scar tissue substitutes healthy liver tissue. This prevents the liver from functioning normally. Cirrhosis inhibits the circulation of blood through the liver because scar tissue forms. The liver gradually loses its ability to function at all. In severe situations, the liver is so destroyed that it no longer functions.
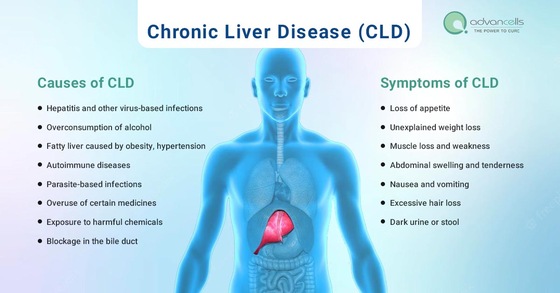
Causes of CLD
The most prevalent causes of chronic liver diseases are:
- Hepatitis and other virus-based infections
- Overconsumption of alcohol (alcoholic liver cirrhosis)
- Fatty liver caused by obesity, hypertension, or high cholesterol
Other causes include:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Parasite-based infections
- Overuse of certain medicines
- Exposure to harmful chemicals
- Blockage in the bile duct
Symptoms of CLD
If not detected on time, living with liver disease can be challenging. Symptoms vary as the degree of cirrhosis varies from patient to patient. The most well-known symptoms of liver disease are yellowing of skin, nails, and sclera, along with fever and fatigue. Here are some symptoms of acute liver failure that are not very well known.
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Muscle loss and weakness
- Abdominal swelling and tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Excessive hair loss
- Dark urine or stool
Treatments Available for CLD
- SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT
A common symptom of CLD is swelling. Patients are often recommended to completely stop alcohol intake, reduce salt intake, maintain a healthy weight, and take some medicines to reduce the effect of cirrhosis-related swelling in the body. - TRANSPLANT
In cases of advanced cirrhosis, the liver stops functioning completely, a liver transplant is the most common course of treatment. A liver transplant is a surgical procedure done to replace the patient’s diseased liver with a healthy liver. The healthy liver can be taken from a family member or a deceased organ donor.
A patient has to undergo rigorous testing to ensure that it is not alcoholic liver cirrhosis and that the patient will remain healthy after the transplant. - CLD STEM CELL TREATMENT
Introducing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is a promising cell-based therapy for the treatment of chronic liver diseases. The efficacy of MSCs in CLD Stem Cell Treatment is highly dependent on their capability to differentiate into various cell types.
An efficient stem-cell therapy requires cells to be able to:
- differentiate into hepatocytes
- possess their immunosuppressive abilities
- have the capability of secreting the same trophic factors that hepatocytes secrete.
The future potential of stem-cell therapy acting as an efficient choice for CLD treatment has been thoroughly investigated in multiple clinical and pre-clinical trials. The transplant of mesenchymal stem cells has not fully been characterized as an alternative therapy for CLD.
However, research evidence has shown that mesenchymal stem cells do secrete some trophic factors that play a crucial role in liver regeneration for cirrhosis patients. These factors reduce inflammation (a common side effect of liver transplants), inhibit cell death, and reduce the chance of fibrosis in scarred liver tissue. Additionally, the trophic factors secreted by mesenchymal stem cells have been found to actively stimulate angiogenesis and regeneration of liver tissue in diseased livers.

Recent Comments